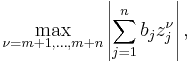Pál Turán
| Paul (Pál) Turán | |
|---|---|
| Born | 18 August 1910 Budapest, Hungary |
| Died | 26 September 1976 (aged 66) Budapest, Hungary |
| Residence | Hungary |
| Nationality | Hungarian |
| Fields | Mathematics |
| Institutions | University of Budapest |
| Alma mater | University of Budapest |
| Doctoral advisor | Lipót Fejér |
| Known for | Power sum method Extremal graph theory |
| Notable awards | Kossuth Prize Tibor Szele Prize |
Paul (Pál) Turán (Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈtuɾaːn]; 18 August 1910–26 September 1976)[1]:271[2] was a Hungarian mathematician who worked primarily in number theory. He had a long collaboration with fellow Hungarian mathematician Paul Erdős, lasting 46 years and resulting in 28 joint papers.[3]
Contents |
Life and education
Turán was born in Budapest on 18 August 1910.[1]:271 He received a teaching degree at the University of Budapest in 1933 and the Ph.D. degree under Lipót Fejér in 1935.[1]:271 As a victim of numerus clausus, he could not get university job for several years. He was sent to labour service at various times from 1940 to 1944. He is said to have been recognized and perhaps protected by a fascist guard, who, as a mathematics student, had admired Turán's work.[4]
He became associate professor at the University of Budapest in 1945 and full professor in 1949.[1]:272 He married mathematician Vera Sós in 1952 and they have two children.[5]:20
He died in Budapest on 26 September 1976[1]:271 of leukemia.[6]:8
Work
Turán worked primarily in number theory,[6]:4 but also did much work in analysis and graph theory.
Number theory
In 1934 Turán gave a new and very simple proof of a 1917 result of G. H. Hardy and Ramanujan on the normal order of the number of distinct prime divisors of a number n, namely that it is very close to ln ln n. In probabilistic terms he estimated the variance from ln ln n. Halász says "Its true significance lies in the fact that it was the starting point of probabilistic number theory". [7]:16 The Turán–Kubilius inequality is a generalization of this work.[6]:5 [7]:16
Turán was very interested in the distribution of primes in arithmetic progressions, and he coined the term "prime number race" for irregularities in the distribution of prime numbers among residue classes.[6]:5 With his coauthor Knapowski he proved results concerning Chebyshev's bias.
The Erdős–Turán conjecture makes a statement about primes in arithmetic progression.
Much of Turán's number theory work dealt with the Riemann hypothesis and he developed the power sum method (see below) to help with this. Erdős said "Turán was an 'unbeliever,' in fact, a 'pagan': he did not believe in the truth of Riemann's hypothesis."[3]:3
Analysis
Much of Turán's work in analysis was tied to his number theory work. Outside of this he proved Turán's inequalities relating the values of the Legendre polynomials for different indices, and, together with Paul Erdős, the Erdős–Turán equidistribution inequality.
Graph theory
Erdős wrote of Turán, "In 1940–1941 he created the area of extremal problems in graph theory which is now one of the fastest-growing subjects in combinatorics."[3]:4 The field is known more briefly today as extremal graph theory. Turán's best-known result in this area is Turán's Graph Theorem, that gives an upper bound on the number of edges in a graph that does not contain the complete graph Kr as a subgraph. He invented the Turán graph, a generalization of the complete bipartite graph, to prove his theorem. He is also known for the Kövari–Sós–Turán theorem bounding the number of edges that can exist in a bipartite graph with certain forbidden subgraphs, and for raising Turán's brick factory problem, namely of determining the crossing number of a complete bipartite graph.
Power sum method
Turán developed the power sum method to work on the Riemann hypothesis.[7]:9–14 The method deals with inequalities giving lower bounds for sums of the form
hence the name "power sum".[8]:319 Besides its applications in analytic number theory, it has been used in function theory, numerical analysis, differential equations, transcendence theory, and estimating the number of zeroes of a function in a disk.[8]:320
Publications
- Ed. by P. Turán. (1970). Number Theory. Amsterdam: North-Holland Pub. Co. ISBN 9780720420371.
- Paul Turán (1984). On a New Method of Analysis and Its Applications. New York: Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 9780471892557. Deals with the power sum method.
- edited by Paul Erdős. (1990). Collected Papers of Paul Turán. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó. ISBN 9789630542982.
Honors
- Hungarian Academy of Sciences elected corresponding member in 1948 and ordinary member in 1953[1]:272
- Kossuth Prize in 1948 and 1952[1]:272
- Tibor Szele Prize of János Bolyai Mathematical Society 1975[1]:272
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h Alpár, L. (August 1981). "In memory of Paul Turán". Journal of Number Theory (Academic Press) 13 (3): 271–278. doi:10.1016/0022-314X(81)90012-3.
- ^ "Magyar Életrajzi Lexikon: Turán Pál" (in Hungarian). Magyar Elecktronikus Könyvtár (Hungarian Electronic Library). http://mek.oszk.hu/00300/00355/html/ABC15363/16089.htm. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
- ^ a b c Erdős, Paul (1980). "Some notes on Turán's mathematical work". Journal of Approximation Theory 29 (1): 2–6. doi:10.1016/0021-9045(80)90133-1. http://www.renyi.hu/~p_erdos/1980-42.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ "An officer was standing nearby, watching us work. When he heard my name, he asked the comrade whether I was a mathematician. It turned out, that the officer, Joshef Winkler, was an engineer. In his youth, he had placed in a mathematical competition; in civilian life he was a proof-reader at the print shop where the periodical of the Third Class of the Academy (Mathematical and Natural sciences) was printed. There he had seen some of my manuscripts." P. Turán, "A note of welcome", Journal of Graph Theory 1 (1977), pp. 7-9.
- ^ Babai, László (2001). "In and Out of Hungary: Paul Erdős, His Friends, and Times" (PostScript). University of Chicago. http://www.cs.uchicago.edu/files/tr_authentic/TR-2001-03.ps. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ a b c d Erdős, Paul (1980). "Some personal reminiscences of the mathematical work of Paul Turán". Acta Arithmetica 37: 3–8. ISSN 0065-1036. http://www.renyi.hu/~p_erdos/1980-43.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ a b c Halász, G. (1980). "The number-theoretic work of Paul Turán". Acta Arithmetica 37: 9–19. ISSN 0065-1036. http://www.numbertheory.org/obituaries/AA/turan/turan_halasz/index.html. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- ^ a b Tijdeman, R. (April 1986). "Book reviews: On a new method of analysis and its applications" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society (Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society) 14 (2): 318–322. doi:10.1090/S0273-0979-1986-15456-X. http://projecteuclid.org/DPubS/Repository/1.0/Disseminate?view=body&id=pdf_1&handle=euclid.bams/1183553181. Retrieved 2008-06-22.